
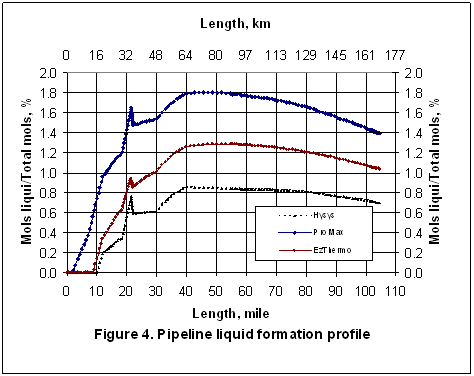

The elevation difference between the field and separation-nearly 1,000 m-allows easy multiphase shipment without slugging. The field has 18 active wells producing at a condensate-gas ratio of 252 bbl/million cu m. A maximum 18.7 million cu m/day (MMcmd) travels through the line, equivalent to the field's peak winter production. OD pipe with the remaining 41 km using 26-in. 1 shows its elevation profile, while Tables 1 and 2 display fluid analysis and pipe condition, respectively. The pipeline is 63 km long and buried at 1 m. The studied pipeline is in southern Iran, moving natural gas from a production field to a separation plant where gas, condensate, and water are separated without chemical treatment. 6-7 To compare the two simulators, this article uses only Olga's steady-state function, applying both it and Pipesim to an actual multiphase wet gas transmission pipeline and comparing the results with those of field data for a range of gas flow rates. Users of both Pipesim and Olga, however, have noted differences in output even when using the same mass flow rates, gas-liquid compositions, and geometrical data. The history-matched model Amapetco built allowed it to increase network capacity and cut expenses. Simulation scenarios included gas only, oil only, and multiphase flow. 4 The company also sought to overcome flow assurance problems brought about by hydrate formation and other issues.
#Pipesim erosional velocity ratio full#
(Amapetco) in Egypt last year used Pipesim in an effort to optimize multiphase subsea flow and produce its reservoirs to full potential. Careless selection of existent correlations and equations, however, without attention to the nature of the issue, may lead to considerable errors in prediction results. An accurate simulation or prediction can help in the design of the pipe network and in selection of the proper solution to potential operating problems. Predicting the behavior of a multiphase system, even in steady state, is complex. These changes make liquid and solid hydrate formation probable, 2 in turn creating an unsteady pressure profile in the pipe. 1 Frictional loss, elevation change, Joule-Thomson effect, and heat exchange between the pipe and its surroundings lead to pressure and temperature changes. In the movement of natural gas through pipes, the associated pressure and temperature of the fluid flow are subject to change throughout the pipe.
#Pipesim erosional velocity ratio software#
Pressure-drop predictions can vary greatly depending on the software used. Gas flow rate can affect liquid holdup and thus pressure-drop prediction. Pipesim, however, does not reliably predict pressure drop at low natural gas flow rates and should be matched with field data to ensure accurate predictions. Olga software can be used to simulate multiphase pipeline flow at a wide range of rates without the need to match results to field data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
